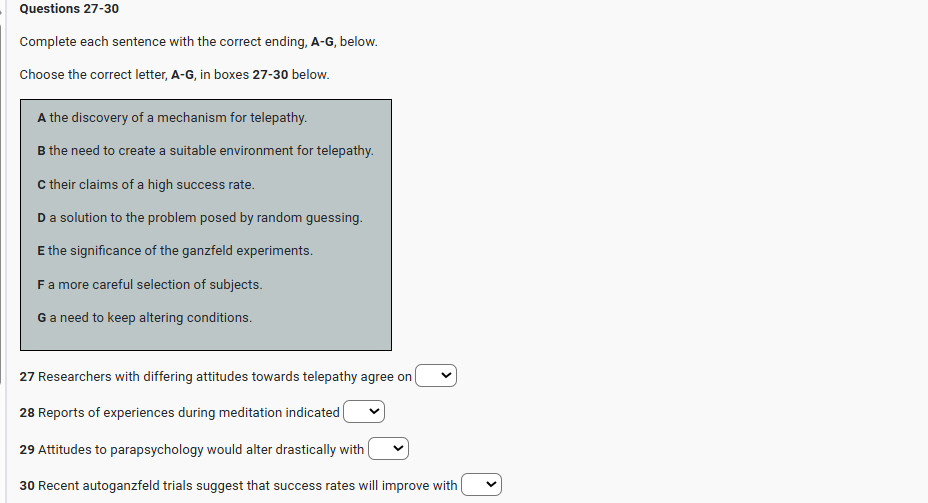
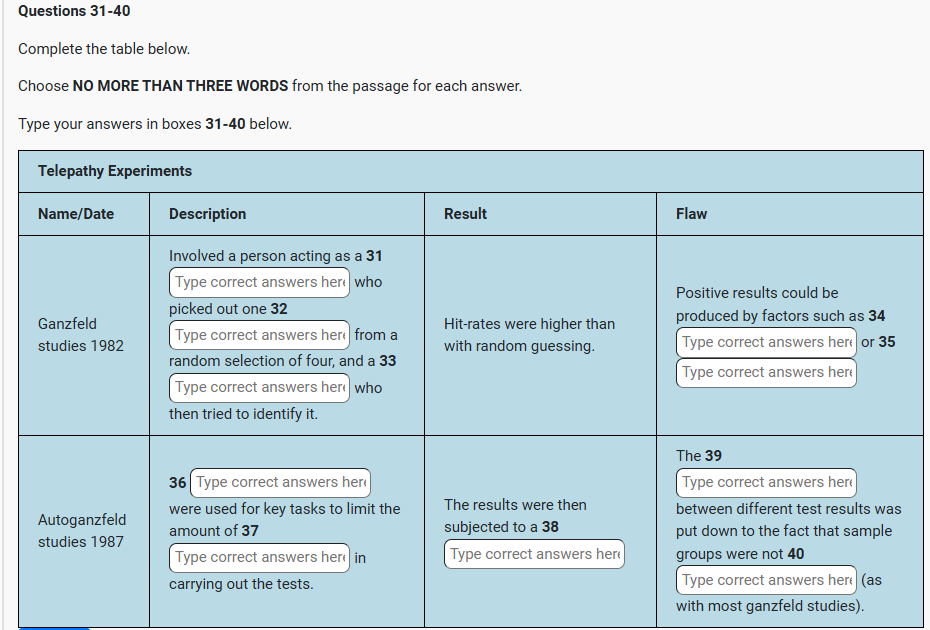
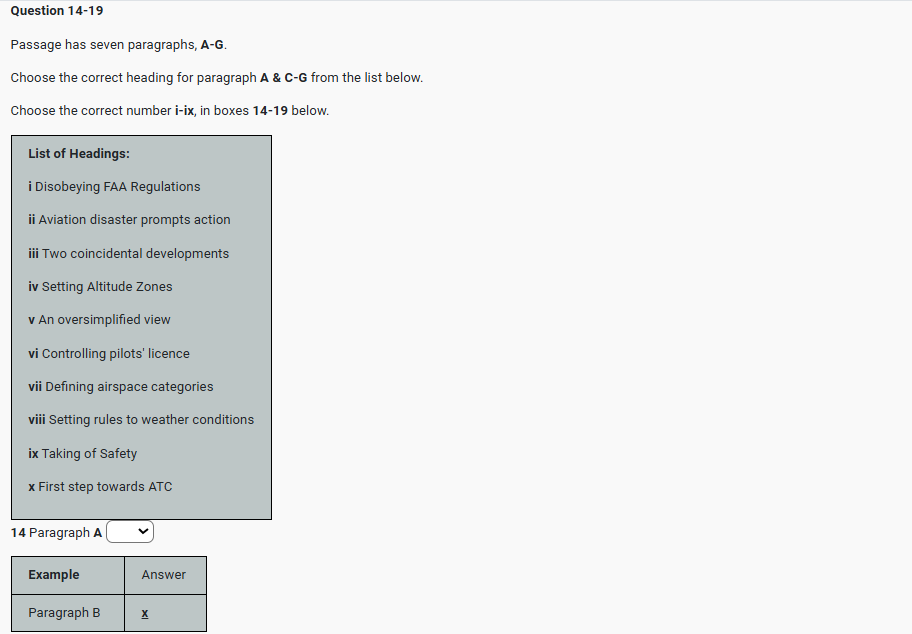
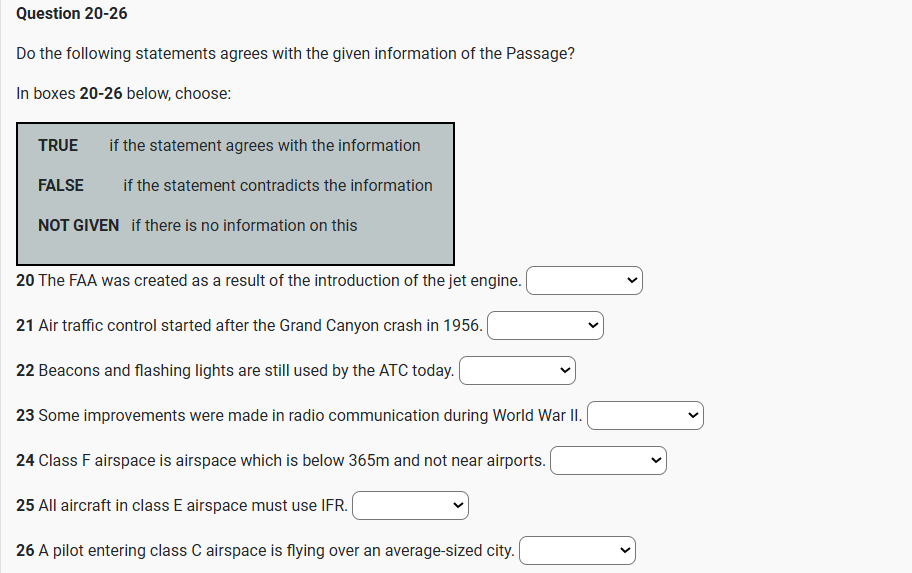
IELTS READING – THE LITTLE ICE AGE S42AT2

|
IELTS Reading THE LITTLE ICE AGE reading practice test has 10 questions belongs to History & Environmental Science subject.. |
A. This book will provide a detailed examination of the Little Ice Age and other Q20 climatic shifts, but, before I embark on that, let me provide a historical context. We tend to think of climate – as opposed to weather – as something unchanging, yet humanity has been at the mercy of climate change for its entire existence, with at least eight glacial episodes in the past 730,000 years. Our ancestors adapted to the universal but irregular global warming since the end of the last great Ice Age, around 10,000 years ago, with dazzling opportunism. They developed strategies for surviving harsh drought cycles, decades of heavy rainfall, or unaccustomed cold; adopted agriculture and stock-raising, which revolutionised human life; and founded the world’s first pre-industrial civilisations in Egypt, Mesopotamia, and the Americas. But the price of sudden climate change, in famine, disease, and suffering, was often high.
B. The Little Ice Age lasted from roughly 1300 until the middle of the nineteenth century. Only two centuries ago, Europe experienced a cycle of bitterly cold winters; mountain glaciers in the Swiss Alps were the lowest in recorded memory, and pack ice surrounded Iceland for much of the year. Q14 The climatic events of the Little Ice Age did more than help shape the modern world. They are the deeply important context for the current unprecedented global warming. The Little Ice Age was far from a deep freeze, however; rather an irregular seesaw of rapid climatic shifts, few lasting more than a quarter-century, driven by complex and still little understood interactions between the atmosphere and the ocean. The seesaw brought cycles of intensely cold winters and easterly winds, then switched abruptly to years of heavy spring and early summer rains, mild winters, and frequent Atlantic Q21 storms, or to periods of droughts, light northeasterly winds, and summer Q22 heat waves.

C. Reconstructing the climate changes of the past is extremely difficult, because systematic weather observations began only a few centuries ago, in Europe and North America. Records from India and tropical Africa are even more recent. For the time before records began, we have only ‘proxy records’ reconstructed largely from Q18 tree rings and Q19 ice cores, supplemented by a few incomplete written accounts. We now have hundreds of tree-ring records from throughout the northern hemisphere, and many from south of the equator, too, amplified with a growing body of temperature data from ice cores drilled in Antarctica, Greenland, the Peruvian Andes, and other locations. We are close to a knowledge of annual summer and winter temperature variations over much of the northern hemisphere going back 600 years.
D. Q15 This book is a narrative history of climatic shifts during the past ten centuries, and some of the ways in which people in Europe adapted to them. Q25 Part One describes the Medieval Warm Period, roughly 900 to 1200. During these three centuries, Norse voyagers from Northern Europe explored northern seas, settled Greenland, and visited North America. It was not a time of uniform warmth, for then, as always since the Great Ice Age, there were constant shifts in rainfall and temperature. Mean European temperatures were about the same as today, perhaps slightly cooler.
E. It is known that the Little Ice Age cooling began in Greenland and the Arctic in about 1200. As the Arctic ice pack spread southward, Norse voyages to the west were rerouted into the open Atlantic, then ended altogether. Storminess increased in the North Atlantic and the North Sea. Colder, much wetter weather descended on Europe between 1315 and 1319, when thousands perished in a continent-wide famine. By 1400, the weather had become decidedly more unpredictable and stormier, with sudden shifts and lower temperatures that culminated in the cold decades of the late sixteenth century. Fish were a vital commodity in growing towns and cities, where food supplies were a constant concern. Q26 Dried cod and herring were already the staples of the European fish trade, but changes in water temperatures forced fishing fleets to work further offshore. The Basques, Dutch, and English developed the first offshore fishing boats adapted to a colder and stormier Atlantic. A gradual agricultural revolution in northern Europe stemmed from concerns over food supplies at a time of rising populations. The revolution involved intensive commercial farming and the growing of animal fodder on land not previously used for crops. Q16 The increased productivity from farmland made some countries self-sufficient in grain and livestock and offered effective protection against famine.
F. Global temperatures began to rise slowly after 1850, Q23 with the beginning of the Modern Warm Period. There was a vast migration from Europe by land-hungry farmers and others, to which the famine caused by the Irish potato blight contributed, to North America, Australia, New Zealand, and southern Africa. Q24 Millions of hectares of forest and woodland fell before the newcomers’ axes between 1850 and 1890, as intensive European farming methods expanded across the world. Q17 The unprecedented land clearance released vast quantities of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, triggering for the first time humanly caused global warming. Temperatures climbed more rapidly in the twentieth century as the use of fossil fuels proliferated and greenhouse gas levels continued to soar. The rise has been even steeper since the early 1980s. The Little Ice Age has given way to a new climatic regime, marked by prolonged and steady warming. At the same time, extreme weather events like Category 5 hurricanes are becoming more frequent.
Learn From Experienced Teacher Best IELTS Coaching Dehradun Best IELTS in Dehradun Uttarakhand GMS Road BEST coaching in Dehradun Apply for Class Courses Today Good Results.
![]()
8439000086
8439000087
7055710003
7055710004
IELTS Simulation 323 GMS Road, Near Ballupur Chowk, Dehradun, India
![]()
email: info at ieltsband7.com
Boost Your Score: Practice IELTS Online with IELTS Simulator Prepare for IELTS Effectively Using IELTS Simulator Ace the IELTS: Try Realistic Practice on IELTS Simulator IELTS Simulator: Online Practice to Improve Your IELTS Score Rocky Bay field trip listening practice test has 10 questions belongs to the Leisure & Entertainment subject. Prepare for IELTS IELTS Test International Experienced Teacher Best Training By CELTA Trainer. Best Results Easily Get Required Score IELTS Exam Dates Available, Small Batch Size with Flexible Time, Professional. Easily Get Required Score I am interested in IELTS Pass with Confidence, Dehradun Small Batch Size with Flexible Time, professional faculty. Learn From Experienced Teacher Best IELTS Coaching Dehradun Best IELTS in Dehradun Uttarakhand GMS Road BEST coaching in Dehradun Apply for Class Courses Today Good Results. Small Batch Size, Flexible Time and Professional IELTS Teacher Best IELTS coaching classes IDP certified British Council trained and CELTA certified experienced trainer. Easily Get Required Score Tel:8439000086 Tel:8439000087 Tel:7055710003 Tel:7055710004 Tel:7055710009