IELTS READING – Population movements and genetics S39AT2

| IELTS Reading Population movements and genetics reading practice test has 10 questions belongs to Genetics & Anthropology subject.. |


A. Study of the origins and distribution of human populations used to be based on archaeological and fossil evidence. Q14 A number of techniques developed since the 1950s, however, have placed the study of these subjects on a sounder and more objective footing. The best information on early population movements is now being obtained from the ‘archaeology of the living body’, the clues to be found in genetic material.
B. Recent work on the problem of when people first entered the Americas is an example of the value of these new techniques. North-east Asia and Siberia have long been accepted as the launching ground for the first human colonisers of the New World’. Q15 But was there one major wave of migration across the Bering Strait into the Americas, or several? And when did this event, or events, take place? In recent years, new clues have come from research into genetics, including the distribution of genetic markers in modern Native Americans.
C. Q16 An important project, led by the biological anthropologist Robert Williams, focused on the variants (called Gm allotypes) of one particular protein -immunoglobin G – found in the fluid portion of human blood. All proteins ‘drift’, or produce variants, over the generations, and members of an interbreeding human population will share a set of such variants. Q16 Thus, by comparing the Gm allotypes of two different populations (e.g. two Indian tribes), one can establish their genetic ‘distance’, which itself can be calibrated to give an indication of the length of time since these populations last interbred.
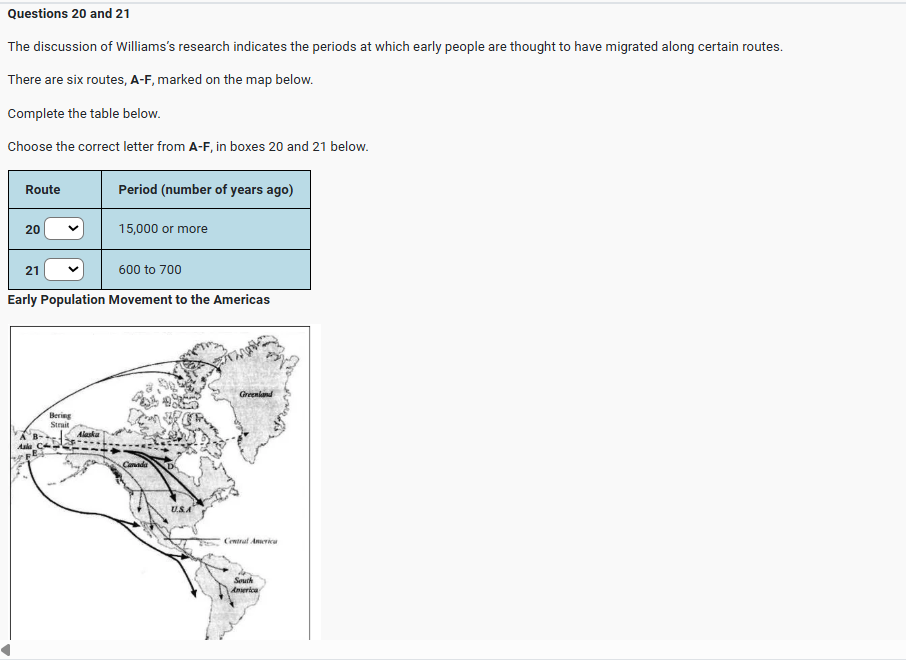
D. Q17 Williams and his colleagues sampled the blood of over 5,000 American Indians in western North America during a twenty-year period. Q17 They found that their Gm allotypes could be divided into two groups, one of which also corresponded to the genetic typing of Central and South American Indians. Other tests showed that the Inuit (or Eskimo) and Aleut formed a third group. Q20 From this evidence it was deduced that there had been three major waves of migration across the Bering Strait. Q24 The first, Paleo-lndian, wave more than 15,000 years ago was ancestral to all Central and South American Indians. Q21&23 The second wave, about 14,000-12,000 years ago, brought Na-Dene hunters, ancestors of the Navajo and Apache (who only migrated south from Canada about 600 or 700 years ago). Q22 The third wave, perhaps 10,000 or 9,000 years ago, saw the migration from North-east Asia of groups ancestral to the modern Eskimo and Aleut.

E. How far does other research support these conclusions? Q18&25 Geneticist Douglas Wallace has studied mitochondrial DNA in blood samples from three widely separated Native American groups: Pima-Papago Indians in Arizona, Maya Indians on the Yucatan peninsula, Mexico, and Ticuna Indians in the Upper Amazon region of Brazil. As would have been predicted by Robert Williams’s work, all three groups appear to be descended from the same ancestral (Paleo-lndian) population.
F. Q19 There are two other kinds of research that have thrown some light on the origins of the Native American population; they involve the study of teeth and of languages. The biological anthropologist Christy Turner is an expert in the analysis of changing physical characteristics in human teeth. He argues that tooth crowns and roots have a high genetic component, minimally affected by environmental and other factors. Q26 Studies carried out by Turner of many thousands of New and Old World specimens, both ancient and modern, suggest that the majority of prehistoric Americans are linked to Northern Asian populations by crown and root traits such as incisor shoveling (a scooping out on one or both surfaces of the tooth), single-rooted upper first premolars and triple-rooted lower first molars.
According to Turner, this ties in with the idea of a single Paleo-lndian migration out of North Asia, which he sets at before 14,000 years ago by calibrating rates of dental micro-evolution. Tooth analyses also suggest that there were two later migrations of Na-Denes and Eskimo-Aleut.

G. The linguist Joseph Greenberg has, since the 1950s, argued that all Native American languages belong to a single ‘Amerind’ family, except for Na-Dene and Eskimo-Aleut – a view that gives credence to the idea of three main migrations. Greenberg is in a minority among fellow linguists, most of whom favour the notion of a great many waves of migration to account for the more than 1,000 languages spoken at one time by American Indians. But there is no doubt that the new genetic and dental evidence provides strong backing for Greenberg’s view. Dates given for the migrations should nevertheless be treated with caution, except where supported by hard archaeological evidence.
Boost Your Score: Practice IELTS Online with IELTS Simulator.
![]()
8439000086
8439000087
7055710003
7055710004
IELTS Simulation 323 GMS Road, Near Ballupur Chowk, Dehradun, India
![]()
email: info at ieltsband7.com