IELTS LISTENING- Space Traffic Management S73T4
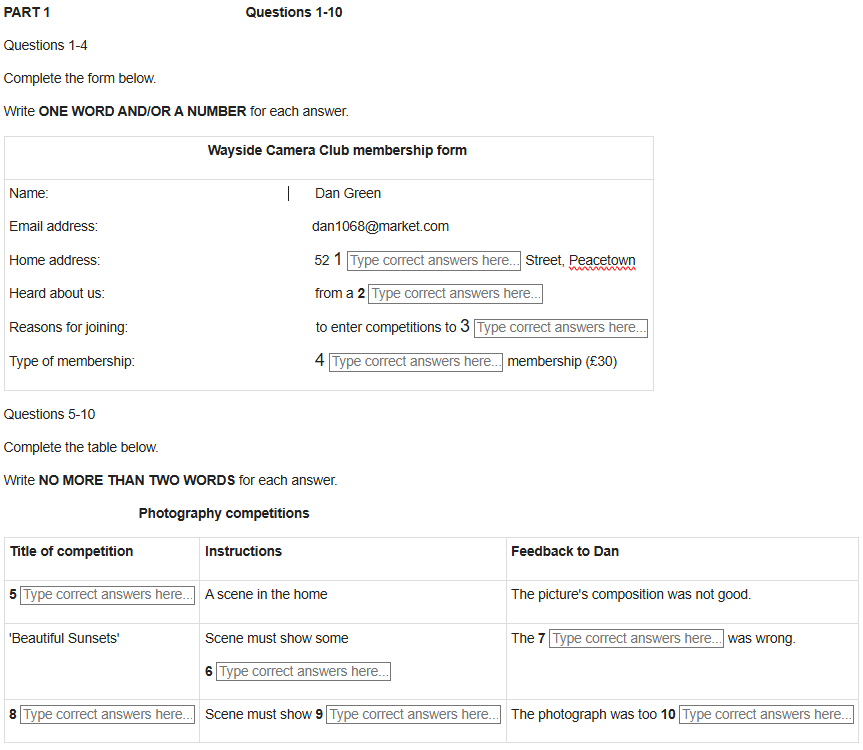
| IELTS LISTENING – Space Traffic Management listening practice test has 10 questions belongs to the Science & Technology subject.. |
In today’s astronomy lecture, I’m going to talk about the need for a system to manage the movement of satellites and other objects in orbit around the Earth. In other words, a Space Traffic Management system. We already have effective Air Traffic Control systems that are used internationally to ensure that planes navigate our skies safely. Well, Space Traffic Management is a similar concept, but focusing on the control of satellites.
The aim of such a system would be to prevent the danger of collisions in space between the objects in orbit around the Earth. In order to do this, we’d need to have a set of legal measures, and we’d also have to develop the technical systems to enable us to prevent such accidents. Q31
But unfortunately, at present we don’t actually have a Space Traffic Management system that works. So why not? What are the problems in developing such a system?
Well, for one thing, satellites are relatively cheap these days, Q32 compared with how they were in the past, meaning that more people can afford to put them into space. So there’s a lot more of them out there, and people aren’t just launching single satellites but whole constellations, consisting of thousands of them designed to work together. So space is getting more crowded every day. Q33
But in spite of this, one thing you may be surprised to learn is that you can launch a satellite into space and, once it’s out there, it doesn’t have to send back any information to Earth to allow its identification. Q34 So while we have international systems for ensuring we know where the planes in our skies are, and to prevent them from colliding with one another, when it comes to the safety of satellites, at present we don’t have anything like enough proper ways of tracking them. Q35

And it isn’t just entire satellites that we need to consider. A greater threat is the huge amount of space debris in orbit around the Earth – broken bits of satellite and junk from space stations and so on. And some of these are so small that they can be very hard to identify, but they can still be very dangerous.
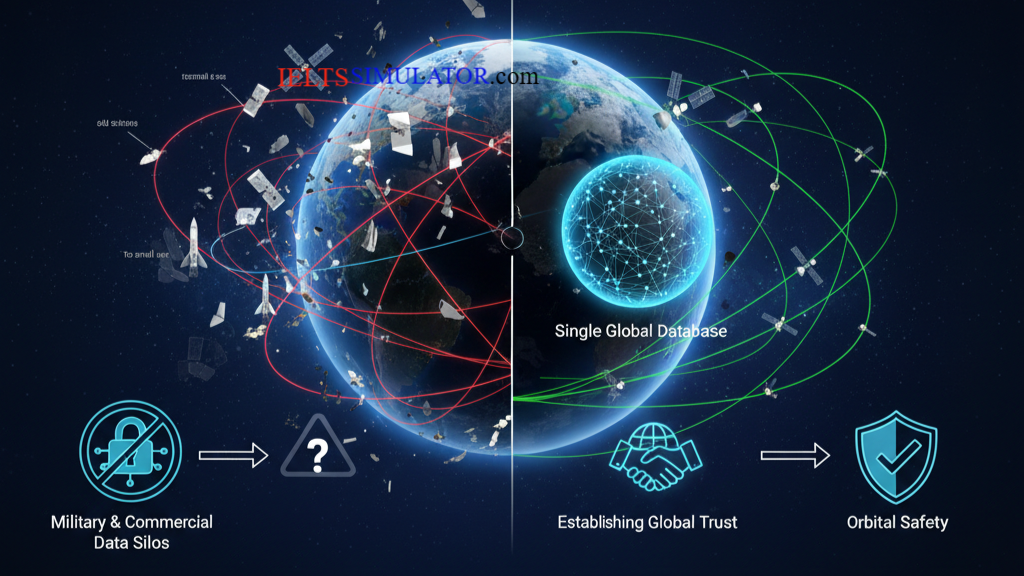
In addition, some operators may be unwilling to share information about the satellites they’ve launched. For example, a satellite may be designed for military purposes, or it may have been launched for commercial reasons, and the operators don’t want competitors to have information about it. Q36
And even if the operators are willing to provide it, the information isn’t easy to collect. Details are needed about the object itself, as well as about its location at a particular time – and remember that a satellite isn’t very big, and it’s likely to be moving at thousands of kilometres an hour. Q37 We don’t have any sensors that can constantly follow something moving so fast, so all that the scientists can do is to put forward a prediction concerning where the satellite is heading next. Q38
So those are some of the problems that we’re facing. Let’s consider now some of the solutions that have been suggested. One key issue is the way in which information is dealt with. We need more information, but it also needs to be accessible at a global level, so we need to establish shared standards that we can all agree on for the way in which this information is presented. We already do this in other areas of science, so although this is a challenge, it’s not an impossible task. Then, as all this information’s collected, it needs to be put together so it can be used, and that will involve creating a single database on which it can be entered. Q39
As we continue to push forward new developments, congestion of the space environment is only going to increase. To cope with this, we need to develop a system like the one I’ve described to coordinate the work of the numerous spacecraft operators, but it’s also essential that this system is one that establishes trust in the people that use it, both nationally and at a global level. Q40
One interesting development.
Learn From Experienced Teacher Best IELTS.
Small Batch Size, Flexible Time.
![]()
8439000086
8439000087
7055710004
IELTS Simulation 323 GMS Road, Near Ballupur Chowk, Dehradun, India
![]()
email: info at ieltsband7.com